Use discount code WELCOME50 for £50 off your first Buy Now order - UK only
When you or a loved one are managing diabetes, you’re likely vigilant about maintaining your blood glucose levels. However, what many people may not realise is that diabetes can have implications far beyond blood sugar control, including serious eye-related complications such as diabetic macular oedema.
In this blog post, we will delve into the connection between macular oedema and diabetes. We’ll discuss what macular oedema is, how it’s caused, how it is linked to diabetes, its symptoms, and available treatments. We hope that through greater understanding, our readers can remain proactive in managing their health and wellbeing, especially regarding their eyes.
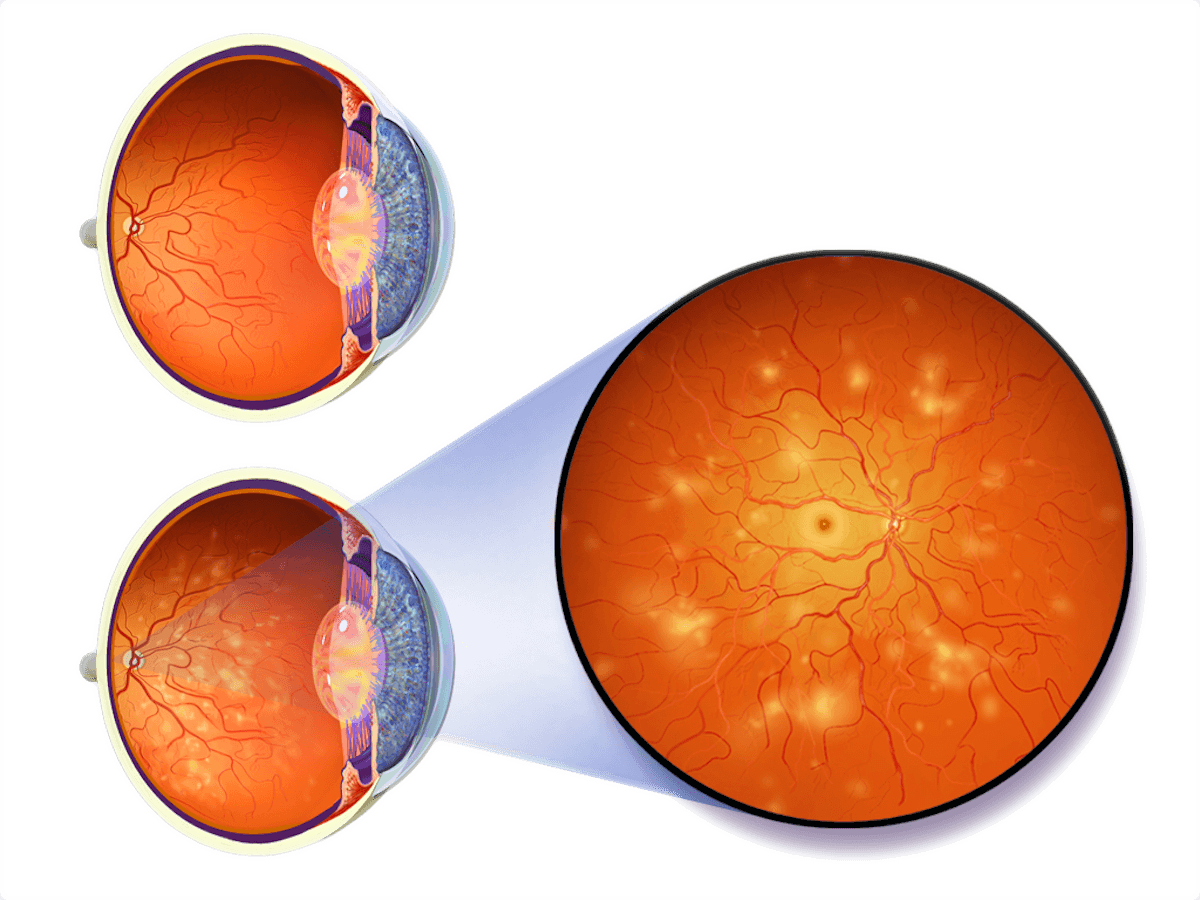
Located at the back of your eye, the macula is the part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision, which lets you read, drive, recognise faces, and see colour. Macular oedema arises when fluid and protein deposits accumulate in the macula, causing it to thicken and swell. As the condition progressively worsens, blurriness and vision loss in the centre of your visual field can occur.
People with diabetes are at risk of developing macular oedema. High blood sugar levels can damage the tiny blood vessels (capillaries) in the retina over time, leading to Diabetic Retinopathy. Uncontrolled, the condition can progress to Diabetic Macular Oedema – a primary cause of vision loss in people with diabetic retinopathy.
In more advanced stages of Diabetic Retinopathy, blood vessels in the retina start to leak fluid or bleed, leading to the swelling of the macula. This condition is known as Diabetic Macular Oedema (DME) and it can cause vision to become blurred or distorted.
The symptoms of macular oedema can vary among individuals. Some may experience slight blurriness, while others may see wavy lines or even have a significant loss of central vision. Many people with early-stage macular oedema may not experience symptoms at all.
Given its elusive nature, it’s crucial to get regular eye check-ups, especially if you’re diabetic. These check-ups generally include a detailed, dilated eye examination and imaging tests like Fundus Photographs and Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) to detect any abnormalities early on.
While macular oedema and its related conditions sound terrifying and overwhelming, there are effective treatments available, including medication, laser therapy and vitrectomy – a surgical procedure to remove the clear gel that fills the eye’s centre when it’s filled with blood or fibrous tissue.
For those who dread the thought of eye injections or surgery, there are non-invasive treatment options, like the Noctura 400 Sleep Mask. This low-level light therapy is designed to alleviate the symptoms of eye diseases like Diabetic Retinopathy, Diabetic Macular Oedema, and Diabetic Maculopathy. The mask works by reducing the retina’s oxygen demand during sleep, thus preventing hypoxia – the condition that causes tissue damage due to lack of oxygen.
Regular eye check-ups, controlling your blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels, along with a healthy lifestyle, can significantly minimise the risk of developing these eye complications. Rest assured, should these conditions occur, treatments like the innovative Noctura 400 sleep mask are potential lifelines that can assist you in maintaining your precious vision.
Remember – prevention is better than cure. Stay proactive, stay informed, and take the necessary steps today for healthier vision, even with diabetes.


